Co-organizer:
North China Electric Power University
Contact us:
T: +86 (0)10 6566 4687
E: event@theiet.org.cn
RPG Trend
On 30 April, the International Energy Agency (IEA) released the Global Energy Review 2020: The Impact of the COVID-19 Crisis on Global energy Demand and Carbon Emissions and noted the following points:
In spite of supply chain and project construction delays caused by the outbreak crisis, global renewable energy generation is expected to grow by nearly 5% in 2020, and renewables will account for about 30% of the world's electricity supply.
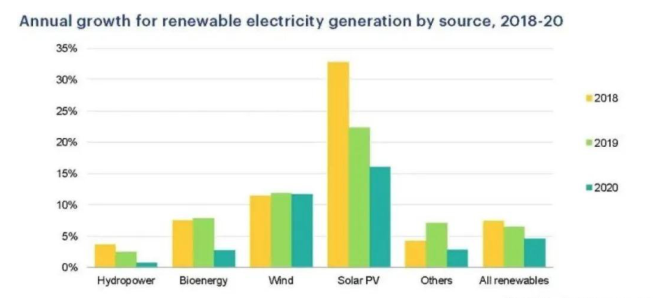
Overall, renewable energy growth was slower than last year, but consistent with the overall slowdown since 2016.Hydropower, which accounts for 60% of all renewable energy generation globally, remains the most uncertain because it depends on rainfall and temperature conditions. PV power generation is expected to grow the fastest (Figure 1), while the absolute increase of wind power generation is the largest.
The contraction in transport activity in the US, Europe and elsewhere will continue to weigh on biofuel consumption, with demand falling sharply throughout the year. The speed of economic recovery has limited impact on renewable energy power generation, but the epidemic prevention and control measures will affect the construction of renewable energy projects.
Source: https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-investment-2020
Downloads:
![]() Session Broadcasting Links.pdf
Session Broadcasting Links.pdf
![]() RPG 2021 Instruction on how to prepare your presentation.pdf
RPG 2021 Instruction on how to prepare your presentation.pdf
RPG Journal:
Impact Factor: 3.894
5-year Impact Factor: 3.981
Cite Score: 7.6
SNIP: 1.301
SJR: 1.682